According to Hicks, utility cannot be measured cardinally because utility which a commodity possesses is subjective and psychological. He, therefore, rejects the quantitative measurement of utility and measures utility ordinally in terms of the indifference curve technique. Total utility is the complete level of satisfaction or value that a person receives from consuming a specific product.

In other words, the utility of an orange to the consumer is twice that of the banana. But this analysis does not hold when there are two different consumers offering two different prices for the same commodity. According to Marshall, the utility of a commodity can be measured in terms of money. If a consumer is willing to pay Rs.2 for an orange and Re 1 for a banana, then the utility of an orange is equal to Rs.2 and that of a banana is Re. Utility is also added by changing the possession of a commodity. But if it is owned by a student of economics, possession utility is created.
Utility: Meaning and Characteristics of Utility
A systematic literature search was performed to identify published CUA studies targeting Asian populations. Information was extracted for both the general characteristics of selected studies and the characteristics of reported HSU data. The percentage of nonreporting was calculated and compared over two time periods (1990–2010 vs 2011–2020). Then using marginal economic utility definition deduction, the company should set a higher price for the chosen product by the customers.
- For example, the consumption of wine possesses utility for a man habitual to drinking because it satisfies his want to drink.
- Time utility is the satisfaction that a product offers to a consumer based on when they receive the product.
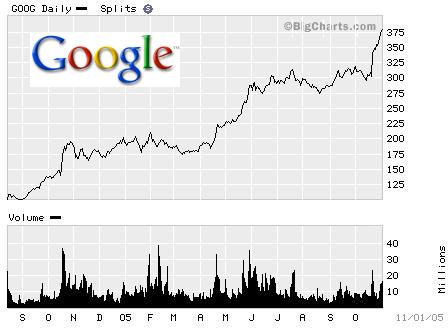
- Panel (a) of Figure 7.1 “Total Utility and Marginal Utility Curves” shows the total utility Henry Higgins obtains from attending movies.
- Over the past two decades, the number of CUA studies targeting Asian populations significantly increased and the methods used to derive HSUs in those studies improved.
Similarly a strictly vegetarian person has no utility for mutton or chicken. Options trading entails significant risk and is not appropriate for all customers. Customers must read and understand the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options before engaging in any options trading strategies. Options transactions are often complex and may involve the potential of losing the entire investment in a relatively short period of time.
Characteristics of health-state utilities used in cost-effectiveness analyses: a systematic review of published studies in Asia
This means the consumer has reached the point of saturation. The studies included in this review were published between 1999 and 2019, with the majority published in the period 2017 to 2019 (43.9%) or 2014 to 2016 (26.6%). There was a significant increase in the number of studies after 2013 (Fig. 2). Most of the CUA studies targeted the population of mainland China (27.0%), Japan (20.8%), or Thailand (9.3%).
Economics as a science remains neutral between good and bad ends products. Hence, the power of a product, good or bad, which can be used to satisfy a human want is known as utility. But cigarette lacks usefulness because it is not useful for the health.
Total utility
It refers to the additional utility on account of the consumption of an additional unit of a commodity. Utility is a relative concept, this means that it differs from individual to individual, from location to location, and from period to period. We can explain his decision using the model of utility-maximizing behavior; Mr. Zane’s out-of-pocket commuting budget constraint is about $2. By reallocating his $2 commuting budget, the gain in utility of having more time at home exceeds the loss in utility from not sipping premium coffee on the way to work.
In other words, the more of a thing we have, the less we want it. When a want is unsatisfied or more intense, there is a greater urge to demand a particular commodity which satisfies a given want. In modern time utility has been called as ‘expected satisfaction.’ Expected satisfaction may be less or equal to or more than the real satisfaction. In economics utility is the capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants. Utility explains why similar goods can have entirely different supply, demand, and price curves. It also explains why people will generally pay a lot of money for scarce goods.
Maximizing Utility
Utility of a commodity depends on a consumer’s mental attitude and assessment regarding its power to satisfy his particular want. Thus, utility of a commodity may differ from person to person. Psychologically, every consumer has his likes and dislikes and everyone determines his own level of satisfaction.
By using less of one commodity, the use of the other cannot be increased. Consequently, he buys less of those goods which give more utility. To achieve this objective he must utilize different factors of production in such a way that the marginal productivity of each factor is equal. It is the reality of a man’s life that is referred to in economics as the law of Diminishing Marginal Utility. Utility is abstract which cannot be seen with eyes, or touched or felt with hands.
Economic Utility Definition Types of Utility And Marginal Utility
From the 6 types of utility, this kind explains or check the availability of services and products when customers want them. Consumers need the products according to the weather conditions and season. Utils are imaginary and characteristics of utility psychological units that are used to measure satisfaction obtained from the consumption of a certain quantity of a commodity. Economists assume that consumers behave in a manner consistent with the maximization of utility.
A bag of chips costs $0.75 and a candy bar costs $0.50 from the vending machines on campus. He has been purchasing an average of 6 bags of chips and 7 candy bars each week. Mr. Juárez is a careful maximizer of utility, and he estimates that the marginal utility of an additional bag of chips during a week is 6. In your answers use B to denote candy bars and C to denote potato chips.
The utility is based on the cardinal approach and wherein utility is measured in terms of money. Suppose Bhanu offers Rs.2 for a banana for which Gautam is prepared to pay Re. 1.The higher price paid by Bhanu does not mean that he gets more utility and Gautam less utility. It simply measures the intensity of our desire for a commodity. Despite this weakness, money is used as a measure of utility. It means utility of a commodity differs from person to person.
This contrasts with marginal utility, which is the value that someone gets from using an additional unit of a product. One way that economists try to assign utility values to products is by looking at the maximum price a consumer will pay for a product. If someone is willing to pay $50 for a hockey ticket, they may decide that they receive 50 units of utility from it. If they would only pay $30 for a baseball ticket, they only get 30 units of satisfaction from seeing a baseball game. Because economists cannot assign objectively accurate values to products or services, they use utility as a concept to explain economic phenomena.
Fitch Affirms Lincoln Electric System, NE’s Revenue Bonds at ‘AA’ – Fitch Ratings
Fitch Affirms Lincoln Electric System, NE’s Revenue Bonds at ‘AA’.
Posted: Fri, 04 Aug 2023 16:53:00 GMT [source]
The utility definition in economics is derived from the concept of usefulness. An economic good yields utility to the extent to which it’s useful for satisfying a consumer’s want or need. Various schools of thought differ as to how to model economic utility and measure the usefulness of a good or service. Marginal Utility is the utility derived from the additional unit of a commodity consumed.
The slope between 6 and 7 movies is zero; the total utility curve between these two quantities is horizontal. The utility it measures will not be a characteristic of particular goods, but rather of each consumer’s reactions to those goods. The utility of a peach exists not in the peach itself, but in the preferences of the individual consuming the peach. One consumer may wax ecstatic about a peach; another may say it tastes OK.
Because consumers can be expected to spend the budget they have, utility maximization is a matter of arranging that spending to achieve the highest total utility possible. If a consumer decides to spend more on one good, he or she must spend less on another in order to satisfy the budget constraint. An indirect utility function gives the optimal attainable value of a given utility function, which depends on the prices of the goods and the income or wealth level that the individual possesses. This conception of utility was not quantified, but a qualitative property of an economic good. The assumption that consumers are fully rational is not correct.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!